Apwh unit 5 study guide – Prepare for success in APWH Unit 5 with our comprehensive study guide. Embark on a journey through global interactions, revolutions, industrialization, imperialism, and more, gaining a deeper understanding of the forces that have shaped our world.
Our study guide provides an in-depth exploration of the key themes and topics covered in APWH Unit 5, equipping you with the knowledge and insights you need to excel in your studies.
Unit Overview
Unit 5 of AP World History, titled “An Age of Revolutions, 1750-1914,” explores a transformative period in global history marked by profound social, political, and economic changes. This unit delves into the causes and consequences of major revolutions, including the American, French, Haitian, and Industrial Revolutions, examining their impact on the political, social, and economic landscapes of the world.
For the upcoming APWH Unit 5 exam, make sure to brush up on your knowledge with a comprehensive study guide. The AP Human Geo Unit 5 FRQ is an excellent resource for practicing the types of questions you’ll encounter. With its detailed explanations and helpful examples, this guide will give you the confidence you need to ace the exam and master APWH Unit 5.
Key Themes and Topics
Unit 5 covers a wide range of themes and topics, including:
- The Enlightenment and its impact on revolutionary thought
- The causes and consequences of the American Revolution
- The French Revolution and the rise of democracy
- The Haitian Revolution and the abolition of slavery
- The Industrial Revolution and its impact on society and the economy
- The rise of nationalism and imperialism
- The social and cultural impact of revolutions
Global Interactions
European colonialism profoundly reshaped the Americas, Africa, and Asia. It introduced new technologies, diseases, and political systems, often disrupting local societies and economies. The establishment of European colonies led to the displacement and exploitation of indigenous populations, as well as the introduction of new crops and livestock.
Trade and Technology
Trade and technology played crucial roles in shaping global interactions. The development of maritime technologies enabled Europeans to explore and establish trade routes around the world. The exchange of goods, ideas, and technologies had a profound impact on both European and non-European societies.
Columbian Exchange
The Columbian Exchange refers to the transfer of plants, animals, and diseases between the Americas, Europe, and Africa following Christopher Columbus’s voyages. This exchange had significant consequences for both hemispheres, introducing new crops like corn and potatoes to Europe, while also bringing diseases like smallpox and measles to the Americas.
Revolutions and Reform
Revolutions and reform movements have played a pivotal role in shaping global history, leading to the overthrow of oppressive regimes, the establishment of new political systems, and the expansion of individual rights and freedoms. This section will delve into three significant revolutions and reform movements: the American Revolution, the French Revolution, and reform movements in Latin America.
The American Revolution
The American Revolution, which began in 1775, was a watershed moment in world history. The American colonists, dissatisfied with British rule and its perceived infringements on their liberties, launched a war for independence. Key causes of the revolution included:
Political grievances
The colonists resented the lack of representation in the British Parliament, which led to taxation without representation.
Economic issues
British mercantilist policies hindered the economic growth of the colonies, creating resentment among colonists.
Enlightenment ideals
The colonists were influenced by Enlightenment ideas that emphasized individual rights, liberty, and self-government.The American Revolution resulted in the Declaration of Independence in 1776 and the eventual establishment of the United States of America. The revolution had a profound impact on global politics, inspiring other movements for independence and self-determination worldwide.
Industrialization and Social Change

The Industrial Revolution, a period of rapid technological advancements and economic growth, profoundly transformed societies across the globe. This transformation had significant social and economic impacts, leading to the rise of labor movements and new challenges for workers.
Factors Leading to the Industrial Revolution
- Agricultural Revolution: Improved agricultural techniques increased food production, leading to a surplus of labor.
- Technological Innovations: Inventions such as the steam engine and power loom revolutionized production processes.
- Availability of Raw Materials: Access to abundant natural resources, such as coal and iron ore, fueled industrial growth.
- Capital Investment: The accumulation of wealth from trade and agriculture provided the capital necessary for industrial development.
Social and Economic Impacts of Industrialization
Industrialization had far-reaching social and economic consequences:
- Urbanization: Factories drew workers to cities, leading to rapid urban growth and overcrowding.
- New Social Classes: The rise of industrial capitalism created new social classes, including the industrial bourgeoisie and working class.
- Economic Inequality: Industrialization led to increased economic disparities, with factory owners amassing wealth while workers faced low wages and poor working conditions.
Rise of Labor Movements and Workers’ Challenges
As industrialization progressed, workers faced significant challenges:
- Long Working Hours: Factory workers often worked 12-16 hour days in hazardous conditions.
- Low Wages: Wages were often insufficient to meet basic needs, leading to widespread poverty.
- Child Labor: Children were often employed in factories, performing dangerous tasks.
These challenges gave rise to labor movements, as workers organized to demand better working conditions, higher wages, and legal protections.
Imperialism and Nationalism
Imperialism, the domination of one nation over another, has played a significant role in shaping global politics and societies. Driven by economic, political, and social factors, imperialism has had far-reaching consequences for both colonizing and colonized nations.
Causes of Imperialism
- Economic: Desire for new markets, resources, and cheap labor.
- Political: Rivalry between European powers, quest for prestige and influence.
- Social: Belief in the superiority of Western civilization and the “civilizing mission” of Europe.
Consequences of Imperialism
- Political: Division of the world into colonies, rise of nationalism and anti-colonial movements.
- Economic: Exploitation of resources, disruption of local economies, and introduction of new technologies.
- Social: Cultural assimilation, forced labor, and social upheaval.
Role of Nationalism in Shaping Global Politics, Apwh unit 5 study guide
Nationalism, a sense of belonging and loyalty to one’s nation, emerged as a powerful force in the 19th century. It inspired movements for independence and self-determination, challenging the dominance of imperial powers.
Impact of Imperialism on Colonized Peoples
Imperialism had a profound impact on colonized peoples, both positive and negative. While it brought new technologies and infrastructure, it also led to political oppression, economic exploitation, and cultural disruption.
The World Wars and Global Conflict
The World Wars marked a period of unprecedented global conflict, reshaping the political, economic, and social landscapes of the world. The first half of the 20th century witnessed two devastating wars, World War I and World War II, followed by the Cold War, a prolonged period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union.
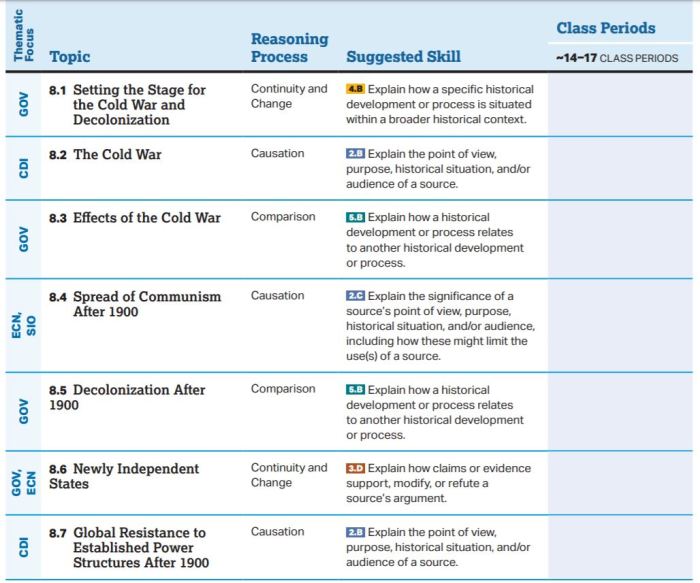
Causes and Consequences of World War I
World War I, fought from 1914 to 1918, was a complex conflict with multiple causes. Nationalism, imperialism, militarism, and a web of alliances contributed to the outbreak of the war. The assassination of Archduke Franz Ferdinand of Austria in 1914 sparked a chain of events that led to the mobilization of millions of troops across Europe.
- Consequences of World War I:
- Death of millions of soldiers and civilians
- Collapse of empires, including the Ottoman, Austro-Hungarian, and Russian empires
- Creation of new nation-states in Europe and the Middle East
- Rise of fascism and communism
- Formation of the League of Nations
Impact of World War II on the Global Order
World War II, fought from 1939 to 1945, was an even more devastating conflict than World War I. The war began with the invasion of Poland by Nazi Germany and escalated into a global conflict involving dozens of countries. The Holocaust, the systematic genocide of European Jews, was a horrific event that occurred during World War II.
- Consequences of World War II:
- Death of an estimated 40-85 million people
- Destruction of cities and infrastructure
- Rise of the United States and the Soviet Union as global superpowers
- Formation of the United Nations
- Decolonization and the rise of new nation-states in Asia and Africa
Rise of the Cold War and Its Impact on International Relations
After World War II, the world entered a period of intense geopolitical rivalry known as the Cold War. The United States and the Soviet Union emerged as the two dominant powers, each leading a bloc of allied nations. The Cold War was characterized by political, economic, and military competition, but it did not escalate into a direct military conflict between the two superpowers.
- Impact of the Cold War on International Relations:
- Division of the world into two spheres of influence
- Nuclear arms race
- Proxy wars and regional conflicts
- Space race
- Ideological struggle between capitalism and communism
Decolonization and the Cold War
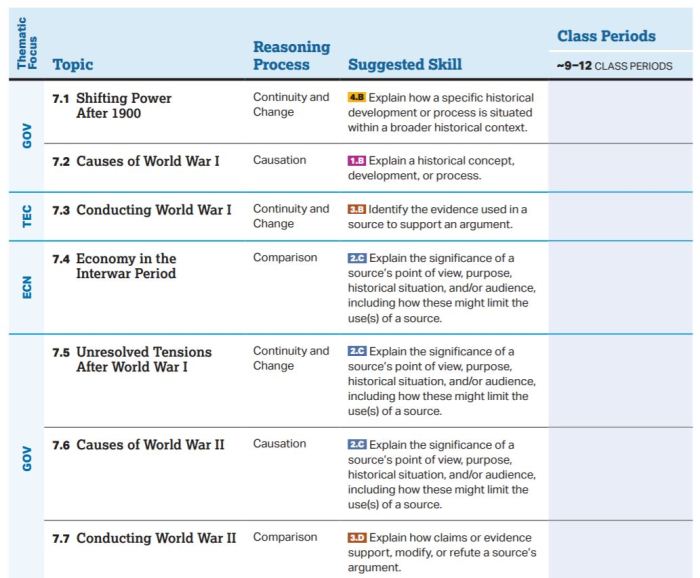
Decolonization, the process of dismantling colonial empires, gained momentum after World War II. This transformation was driven by a confluence of factors, including rising nationalism, anti-colonial movements, and the Cold War rivalry between the United States and the Soviet Union.
Causes of Decolonization
- Nationalism:Growing nationalist sentiments in colonized regions fueled the desire for self-governance and independence.
- Anti-colonial Movements:Organized resistance movements, such as the Indian National Congress and the African National Congress, played a crucial role in mobilizing support for decolonization.
- World War II:The war weakened European colonial powers and exposed the vulnerability of their empires.
- Cold War:The superpowers’ competition for influence extended to newly independent nations, shaping their political and economic trajectories.
Consequences of Decolonization
- Emergence of New Nations:Decolonization led to the creation of numerous new independent states in Asia, Africa, and the Middle East.
- Power Vacuum:The departure of colonial powers left a vacuum, which was often filled by authoritarian regimes or military dictatorships.
- Economic Challenges:Newly independent nations faced significant economic challenges, such as poverty, unemployment, and infrastructure deficiencies.
- Regional Conflicts:Decolonization sometimes exacerbated ethnic and religious tensions, leading to conflicts and civil wars.
Role of the Cold War
The Cold War profoundly influenced the post-colonial world. Superpowers sought to gain influence by supporting client states and spreading their ideologies. This competition often led to proxy wars and fueled regional conflicts.
Challenges and Successes of Newly Independent Nations
Newly independent nations faced a range of challenges, including:
- Establishing Stable Governments:Many new nations struggled to establish stable democratic systems.
- Economic Development:Overcoming poverty and achieving economic growth proved challenging.
- Nation-Building:Creating a sense of national unity and identity among diverse populations.
Despite these challenges, some newly independent nations achieved notable successes:
- India:India emerged as a major regional power and a leader in the non-aligned movement.
- Ghana:Ghana became a symbol of African independence and played a key role in the Organization of African Unity.
- Singapore:Singapore transformed itself into a prosperous economic hub under the leadership of Lee Kuan Yew.
The Global Economy and Interdependence: Apwh Unit 5 Study Guide
Globalization has significantly transformed the world’s economic landscape. It refers to the increasing interconnectedness and interdependence of economies across borders. This interconnectedness has been driven by several factors, including technological advancements, reduced trade barriers, and the rise of multinational corporations.
Factors Leading to Globalization
- Technological Advancements:Improvements in transportation, communication, and information technology have made it easier and cheaper to move goods, services, and capital across borders.
- Reduced Trade Barriers:Free trade agreements and the World Trade Organization (WTO) have played a significant role in reducing tariffs and other trade barriers, facilitating the flow of goods and services between countries.
- Multinational Corporations:The rise of multinational corporations has led to the creation of global supply chains and the integration of production processes across countries.
Global Issues and Challenges

The world faces a multitude of complex and interconnected global issues that demand attention and collaboration. These issues transcend national borders and require collective action to mitigate their impact on humanity and the planet.
Environmental Degradation
Human activities have significantly contributed to environmental degradation, leading to issues such as climate change, pollution, and biodiversity loss. The burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and industrial processes release greenhouse gases into the atmosphere, causing global temperatures to rise and leading to extreme weather events.
Pollution from industrial waste, agricultural runoff, and plastic waste contaminates ecosystems, threatening human health and wildlife. Biodiversity loss is driven by habitat destruction, climate change, and invasive species, resulting in the extinction of countless species and the disruption of ecological balance.
Global Health
The world faces numerous health challenges, including infectious diseases, chronic conditions, and malnutrition. Infectious diseases, such as HIV/AIDS, tuberculosis, and malaria, continue to affect millions worldwide, particularly in developing countries. Chronic conditions, such as heart disease, cancer, and diabetes, are on the rise due to factors like unhealthy diets, physical inactivity, and tobacco use.
Malnutrition, both undernutrition and overnutrition, remains a significant problem, affecting billions of people and contributing to health issues.
Poverty and Inequality
Poverty and inequality are persistent global challenges that hinder human development and social justice. Extreme poverty, defined as living on less than $1.90 per day, affects hundreds of millions of people worldwide. Inequality refers to the unequal distribution of resources, income, and opportunities, leading to disparities in access to education, healthcare, and other essential services.
Poverty and inequality are often interconnected, perpetuating cycles of disadvantage and limiting individuals’ ability to reach their full potential.
Conflict and Violence
Armed conflicts, civil wars, and terrorism continue to plague many regions of the world, causing immense suffering and displacement. Conflicts are often driven by political, ethnic, religious, or economic factors, leading to violence, human rights abuses, and the breakdown of societies.
Terrorism, involving acts of violence intended to instill fear and influence political outcomes, remains a significant threat to global security.
Resource Scarcity
The world’s resources, such as water, energy, and food, are finite and face increasing demand due to population growth and economic development. Water scarcity is a pressing issue in many regions, as climate change and pollution exacerbate droughts and water shortages.
Energy security is also a concern, with the depletion of fossil fuels and the need for sustainable energy sources. Food insecurity affects millions worldwide, particularly in conflict-ridden or disaster-prone areas.
Technological Advancements
While technological advancements have brought many benefits, they also pose challenges. The rapid pace of technological development can lead to job displacement, privacy concerns, and the spread of misinformation. Artificial intelligence, automation, and biotechnology raise ethical questions and require responsible governance to ensure their benefits are harnessed while mitigating potential risks.
Globalization and Interdependence
Globalization has interconnected the world economically, politically, and culturally. While it has facilitated trade, travel, and communication, it has also created challenges. Economic inequality can arise as globalized markets favor certain sectors and regions over others. Cultural homogenization can threaten local traditions and diversity.
Environmental degradation and resource depletion can be exacerbated by global supply chains and consumption patterns.
Demographic Shifts
The world’s population is aging, with increasing numbers of older adults compared to younger generations. This demographic shift has implications for healthcare systems, labor markets, and social security programs. Additionally, migration and urbanization are shaping population dynamics, leading to challenges in managing diversity, providing essential services, and ensuring social cohesion.
Essential Questionnaire
What is the main focus of APWH Unit 5?
APWH Unit 5 covers global interactions, revolutions, industrialization, imperialism, and their impact on the world from the 15th century to the present.
What are the key themes in APWH Unit 5?
Key themes include the impact of European colonialism, the role of trade and technology in shaping global interactions, the causes and consequences of revolutions, the social and economic effects of industrialization, the rise of imperialism and nationalism, and the challenges and successes of decolonization.
How can I prepare for APWH Unit 5?
Use our comprehensive study guide, review your class notes, participate in discussions, and seek additional resources to enhance your understanding of the unit’s content.