Simpson’s diversity index measuring biodiversity answer key – The Simpson’s Diversity Index is a cornerstone in measuring biodiversity, providing a quantitative assessment of species richness and evenness within an ecosystem. It offers ecologists a valuable tool to gauge the health and stability of ecological communities, unraveling the intricate tapestry of life on Earth.
This comprehensive guide delves into the concept, interpretation, and applications of the Simpson’s Diversity Index, empowering readers to harness its potential in ecological studies.
Simpson’s Diversity Index Overview: Simpson’s Diversity Index Measuring Biodiversity Answer Key
The Simpson’s Diversity Index is a quantitative measure of biodiversity that assesses the probability that two randomly selected individuals from a community belong to the same species. It considers both the richness and evenness of species within a community, providing a comprehensive representation of the diversity present.
The mathematical formula for calculating the Simpson’s Diversity Index (D) is:
D = 1
Σ(pi2)
where p irepresents the proportion of individuals belonging to the ith species in the community.
Interpreting Simpson’s Diversity Index
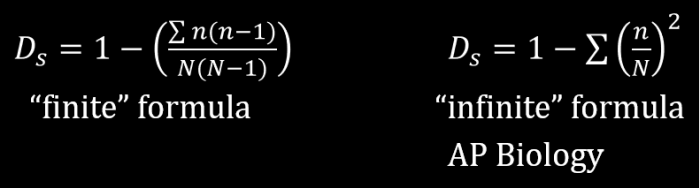
The Simpson’s Diversity Index ranges from 0 to 1, with higher values indicating higher diversity. A value of 0 indicates that all individuals belong to the same species, while a value of 1 indicates that all species are equally represented.
- D < 0.5: Low diversity, with a few dominant species.
- 0.5 ≤ D < 0.75: Moderate diversity, with several common species.
- 0.75 ≤ D < 1: High diversity, with many species evenly represented.
Applications of Simpson’s Diversity Index
The Simpson’s Diversity Index is widely used in ecological studies to measure biodiversity in various ecosystems, including forests, grasslands, and aquatic environments. It provides a standardized metric for comparing the diversity of different communities or assessing changes in diversity over time.
- Monitoring ecosystem health and resilience.
- Evaluating the impact of human activities on biodiversity.
- Assessing the effectiveness of conservation and restoration efforts.
Advantages and Limitations of Simpson’s Diversity Index
Advantages:
- Simple to calculate and interpret.
- Considers both richness and evenness of species.
- Robust to variations in sample size.
Limitations:
- May underestimate diversity in communities with a high number of rare species.
- Assumes random sampling, which may not always be feasible in practice.
Comparison to Other Diversity Indices
The Simpson’s Diversity Index is often compared to other diversity indices, such as the Shannon-Wiener Index and the Gini-Simpson Index.
- Shannon-Wiener Index:More sensitive to rare species but can be more difficult to interpret.
- Gini-Simpson Index:Similar to the Simpson’s Diversity Index but gives more weight to dominant species.
The choice of diversity index depends on the specific research question and the characteristics of the community being studied.
Questions and Answers
What is the range of values for the Simpson’s Diversity Index?
The index ranges from 0 to 1, where 0 indicates no diversity (a single species dominates) and 1 represents maximum diversity (all species are equally abundant).
How does the Simpson’s Diversity Index differ from other diversity indices?
Unlike indices like the Shannon-Wiener Index, which consider only species richness, the Simpson’s Diversity Index also incorporates species evenness, providing a more comprehensive measure of biodiversity.
What are the limitations of the Simpson’s Diversity Index?
The index can be sensitive to sample size and may underestimate diversity in communities with a high number of rare species.